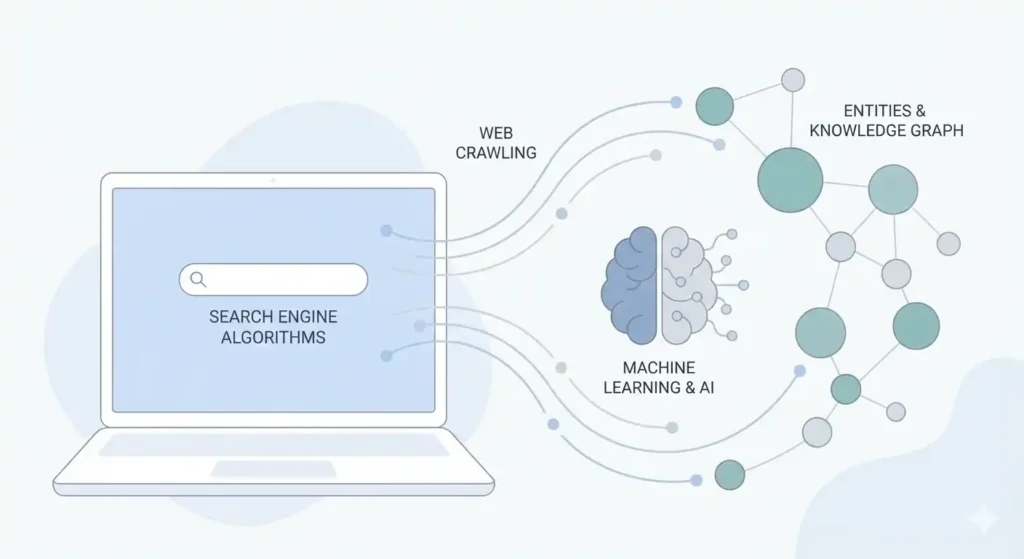
TR;DR – Search engine algorithms are complex systems used by search engines like Google to discover, understand, evaluate, and rank web pages. Modern algorithms rely on AI, machine learning, entity understanding, and quality evaluation systems to determine which pages provide the most useful answers to users, not just which ones use the most keywords.
Introduction
Most articles explain search engine algorithms like a textbook definition.
But Google doesn’t rank textbooks, it ranks pages that satisfy user intent better than competing pages.
Understanding search engine algorithms today isn’t about memorizing update names or chasing ranking factors. It’s about understanding how Google decides your page deserves visibility instead of someone else’s.
Modern search systems are powered by AI, machine learning, entity understanding, and quality classifiers that evaluate usefulness, trust, and intent match at scale. This blog breaks down how search engine algorithms actually work behind the scenes and how SEOs can align with them in 2026 and beyond.
What actually happened in the past that forced Google to rethink search and develop complex algorithms? To understand why Google’s algorithms matter so much today, let’s take a quick look back at the history of search.
Before Search Engines: How the Early Web Worked?
Before modern search engines existed, websites were organized using web directories like early Yahoo.
Sites were submitted manually
Categories were curated by humans
Discovery was slow and incomplete
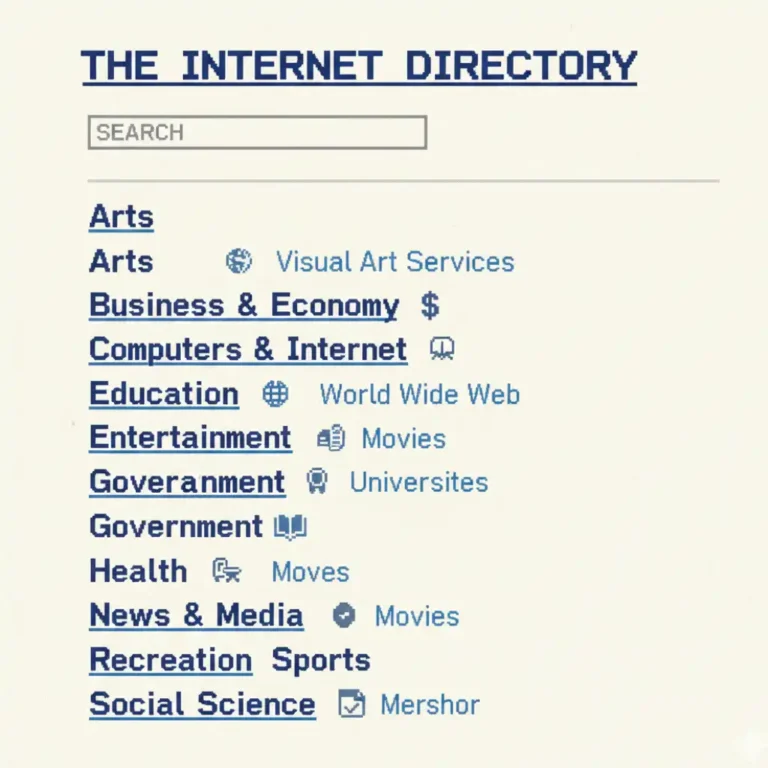
As the web exploded in size, directories couldn’t keep up. Users needed a faster way to find relevant information at scale without human involvement.
This limitation is exactly why automated search algorithms became necessary.
The Birth of Search Engines & Keyword Matching
Early search engines relied heavily on keyword matching. If a page repeated a keyword enough times, it ranked higher regardless of quality.
This led to:
Keyword stuffing
Low-quality content
Poor user experience
Search engines quickly realized that matching words wasn’t enough. They needed to determine which pages were actually useful and trustworthy.
Interestingly, many outdated SEO tactics today still resemble these early systems focusing on repetition instead of real value. Modern algorithms are designed specifically to prevent this.
What Is a Search Engine Algorithm? (Simple Explanation)
A search engine algorithm is a system of rules and signals that determines:
Which pages appear for a search query
In what order they appear
Why one result ranks above another
Think of it like a recipe where each ingredient – relevance, authority, freshness, usability, and intent influences the final outcome.
In reality, it’s not one rule but a combination of intelligent systems working together to decide which content deserves visibility.
How Multiple Algorithms Work Together to Rank Your Page?
There is no single Google algorithm.
Modern search engines operate using hundreds of systems working together, each responsible for specific tasks such as:
Understanding language
Detecting spam
Evaluating content quality
Measuring usefulness
Personalizing results
Some systems run before ranking, some during ranking, and others after results are displayed.
This layered system is why ranking isn’t about a single factor and why content that seems “optimized” can still struggle if it fails in quality or usefulness systems.
How Search Engines Work Today?
Google says Despite their complexity, search engines still follow three core steps:
1. Crawling
Search engines use automated bots (crawlers) to discover pages by following links.
If a page isn’t crawlable, it effectively doesn’t exist to search engines.
2. Indexing
After crawling, search engines analyze and store pages in a massive database called the index.
During indexing, algorithms determine:
What the page is about
Which topics and entities it relates to
How trustworthy it appears
3. Ranking
When a user searches, algorithms evaluate thousands of pages and rank them based on relevance, quality, and intent match all in milliseconds.
However, being indexed does not guarantee strong rankings. Modern systems further evaluate originality, usefulness, and quality before giving pages real visibility.
Understand Cwalability and Indexability here if you have confusion in it.
What Happens Between Indexing and Ranking (Most SEOs Miss This)
Many SEOs think the process ends at indexing. It doesn’t.
After a page enters the index, Google runs it through additional evaluation systems such as:
Content quality classifiers – Does this add value beyond existing results?
Spam detection systems – Does the page look manipulative?
Originality signals – Is this just a rewritten version of other pages?
Usefulness prediction systems – Is this likely to satisfy users?
If a page looks too similar to already-ranked content, Google may keep it indexed but rarely show it.
This is one of the hidden reasons behind “Crawled – currently not indexed” or pages that get impressions but never gain traction.
SEO today is not just about being indexable – it’s about being algorithmically competitive.
How Search Algorithms Understand Meaning (Entities & Context)
Modern algorithms don’t think in keywords, they think in entities.
What is an Entity?
An entity is a real-world concept such as a person, brand, place, or topic.
Entities may include:
- A person
- A brand
- A place
- A topic
For example, “Jaguar” could mean:
- A wild animal
- A luxury car brand
- A sports team
Search algorithms use surrounding words, related entities, and context to understand which “Jaguar” the user means.
If a page mentions engines, models, and car reviews, Google understands the entity as the automobile brand. If it mentions wildlife, habitat, and rainforests, the entity is the animal.
This is why modern SEO focuses on topical depth and related concepts rather than repeating the same keyword over and over.
User Intent: The Core of Modern Search
Every search has intent.
Search engines are designed to identify why someone is searching, not just what they typed.
Common intent types include:
- Informational (learn something)
- Navigational (find a specific site)
- Transactional (buy or convert)
Even a well-written page can struggle if it targets the wrong intent compared to what Google believes users want. Algorithms rank the best intent match, not just the most optimized page.
Pages that fail to satisfy intent, no matter how optimized. Don’t rank long-term.
Personalization: Why Everyone Sees Different Results
Search results aren’t universal anymore.
Algorithms personalize results based on:
- Location
- Language
- Device type
- Search history
- Query freshness
Two people searching the same keyword may see different results, even in the same country.
Because of personalization, SEO is less about ranking #1 for everyone and more about being the best result for the right audience.
This helps search engines surface more relevant information for each individual user.
Key Factors That Influence Search Rankings
While no one knows the exact weighting, modern algorithms commonly evaluate:
- Content relevance & depth
- Entity coverage
- Backlink authority & trust
- User experience (speed, mobile usability)
- Engagement signals (CTR, dwell time)
- Content freshness
- Author and site credibility (EEAT)
None of these factors work alone, they’re evaluated collectively.
Major Google Algorithm Updates (Timeline Overview)
Google’s search system has evolved through major updates:
PageRank (1998) – Introduced link-based authority
Panda (2011) – Targeted low-quality content
Penguin (2012) – Fought spammy backlinks
Hummingbird (2013) – Improved intent understanding
RankBrain (2015) – Introduced machine learning for queries
BERT (2019) – Enhanced language understanding
MUM (2021) – Multimodal AI system
Helpful Content System (2022-Present) – Rewards people-first content
If you wanna learn about these in detail, there are many authentic sources. I personally consult with Google Search Central.
The Real Pattern Behind Google’s Algorithm Updates
| Update | What It Really Improved |
|---|---|
| Panda | Filtering low-value content |
| Penguin | Filtering manipulative links |
| Hummingbird | Understanding search intent |
| RankBrain / BERT | Understanding language and meaning |
| Helpful Content | Rewarding people-first value |
The pattern is clear: Google continues moving toward rewarding pages created to genuinely help users and away from pages created only to manipulate rankings.
The Algorithm Alignment Framework for SEOs (2026 Edition)
Instead of chasing ranking factors, align with the systems Google uses:
| System | What It Evaluates | How to Optimize |
|---|---|---|
| Content Understanding | Topic depth | Cover related subtopics and context |
| Quality Systems | Originality | Add examples, insights, and clarity |
| Trust Systems | Authority | Show expertise and strong brand signals |
| Experience Systems | User satisfaction | Improve speed, design, and readability |
| Spam Systems | Manipulation patterns | Avoid over-optimization |
Winning in modern SEO means performing well across all these systems, not just targeting keywords.
How to Optimize for Search Engine Algorithms in 2026
This is a hot question in the SEO field. With my own experience I tried to answer it in easy words. Well, winning SEO today requires alignment, not manipulation. We should:
Focus on Intent, Not Keywords
Write for users first. Keywords should support clarity, not drive content.
Build Entity-Based Content
Cover topics holistically, not in isolation.
Maintain Content Freshness
Update old pages to reflect current understanding and trends.
Improve User Experience
Fast loading, clean design, and mobile optimization matter.
Strengthen E.E.A.T Signals
Demonstrate experience, expertise, authority, and trust across your site.
As an SEO Person What I’ve Observed in Real SEO Work?
In multiple SEO audits, I’ve seen pages get crawled and indexed but fail to gain visibility because they repeated definitions already covered by stronger sites. Once those pages were improved with clearer intent targeting, original examples, and better structural depth, impressions and rankings began improving within weeks.
Modern algorithms don’t just ask, “Is this relevant?”
They ask, “Is this more useful than what we already have?”
The Return to Search’s Original Purpose
Despite all the AI, machine learning, and personalization, search engines are returning to their original goal:
“Helping users find accurate, useful information as efficiently as possible.”
If your content genuinely serves that purpose, algorithms will eventually align with you, not against you.
FAQ Section
A system of rules and signals search engines use to determine which pages appear in results and in what order, based on relevance, quality, and user intent.
They crawl the web, index content, analyze meaning, evaluate quality and trust, and rank pages based on usefulness and intent match.
Yes. Google makes frequent improvements and larger core updates to refine how quality and relevance are measured.
Many systems, including RankBrain, BERT, and MUM, use AI and machine learning to better understand language and context.
No. Sustainable SEO is about aligning with how algorithms measure usefulness and trust, not exploiting loopholes.
Apply Algorithms Knowledge in Real SEO
Understanding search engine algorithms is the theory. Applying that understanding to real websites in competitive industries is where most businesses struggle.
Ahmad Fraz SEO focuses on building strategies aligned with modern search systems centered on intent, entities, technical clarity, and long-term trust signals.
Instead of chasing updates, the approach is designed to grow with algorithm changes, not break because of them.
Ready to turn algorithm knowledge into real organic growth?
Ahmad Fraz is a seasoned SEO strategist and digital marketing expert with over 9 years of experience helping brands like Dyson, 3M, Marriott, and CureMD achieve measurable growth. Specializing in technical SEO, content strategy, and data-driven optimization, at Ahmad Fraz SEO, he empowers businesses of all sizes to improve visibility, drive qualified traffic, and achieve long-term digital success. His insights and actionable strategies are backed by years of hands-on experience and proven results.
