
If you want to rank in Google, there’s one thing you must understand:
It doesn’t matter what you see on your website – it matters what Googlebot sees.
View page as Googlebot is the concept of checking how Google’s crawler actually accesses, reads, and renders your page. This is critical for technical SEO because many ranking issues happen when content visible to users is invisible or blocked for Googlebot.
In this mini guide, you’ll learn:
- What Googlebot is
- How Googlebot works behind the scenes
- What View Page as Googlebot really means
- How to test your pages like Googlebot
- How robots.txt, noindex, JavaScript, images, and videos affect crawling
- Common Googlebot problems and how to fix them
Let’s go step by step.
What Is Googlebot?
Googlebot is Google’s web crawling system. Its job is to discover, crawl, render, and index web pages so they can appear in Google Search results.
Think of Googlebot as a super-advanced browser that visits your website but with a very specific purpose: understanding content for search indexing, not for human browsing.
Main Types of Googlebot
Google doesn’t use just one crawler. The most important ones are:
- Googlebot Smartphone – Primary crawler (mobile-first indexing)
- Googlebot Desktop – Used in some cases
- Googlebot Image – Crawls images
- Googlebot Video – Crawls video content
This means Google may look at different parts of your site depending on the content type.
How Does Googlebot Work (Step by Step)
To understand View page as Googlebot, you first need to understand how Googlebot processes a page.
1- Discovery of URLs
Googlebot discovers pages through:
- Internal links
- External backlinks
- XML sitemaps
- Previously indexed pages
If a page has no links and isn’t in a sitemap, Googlebot may never find it.
2 – Crawling the Page
Once a URL is discovered, Googlebot tries to access it.
Here’s what happens:
- Googlebot requests the URL from your server
- Your server responds with:
- HTML
- CSS
- JavaScript
- Images and other resources
But before crawling fully, Googlebot checks your robots.txt file.
Example:
User-agent: Googlebot
Disallow: /private/
If a page or resource is disallowed, Googlebot may not crawl it which can affect how the page is rendered.
3 – Rendering (Very Important)
After fetching the raw HTML, Google doesn’t stop there.
It uses a system called the Web Rendering Service (WRS) to render the page similar to how a modern browser runs JavaScript.
This means Googlebot tries to see:
- Hidden content loaded via JavaScript
- Lazy-loaded elements
- Dynamic menus and tabs
But if important files are blocked, rendering breaks.
Example of a bad robots.txt rule:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /js/
Disallow: /css/
If JavaScript and CSS are blocked, Googlebot may see a broken or incomplete version of your site.
4 – Indexing
After rendering, Google decides:
- What the page is about
- Whether it should be indexed
- Which keywords it may rank for
If the page contains a noindex tag, it won’t be added to Google’s index.
Example:
<meta name=”robots” content=”noindex, nofollow”>
This tells Googlebot: “You can crawl, but don’t index this page.”
If you have confusion between crwaling and indexing, you must read: What is the difference between crawlability & indexability
What Does View Page as Googlebot Mean?
View page as Googlebot means seeing your page the way Google’s crawler sees it, not the way a normal user sees it.
A page may look perfect in your browser but be:
- Missing text for Google
- Blocking key resources
- Showing different content to bots
- Not rendering JavaScript properly
Why This Matters for SEO?
If Googlebot can’t properly see your:
- Main content
- Navigation
- Images
- Structured data
Then rankings will suffer even if the page looks great to humans.
How to View a Page as Googlebot (Using Google Search Console)
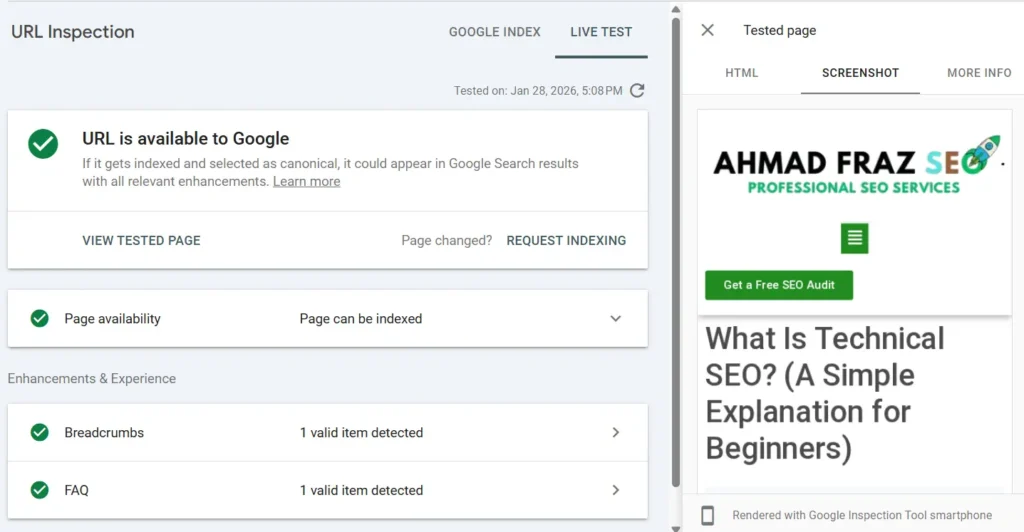
Google no longer uses the old “Fetch as Google” tool, but you can still test pages.
Step-by-Step:
- Open Google Search Console
- Use the URL Inspection Tool
- Enter your page URL
- Click “Test Live URL”
- After the test, click “View Tested Page”
You’ll see:
- HTML Googlebot received
- Screenshot of how Googlebot rendered the page
- List of blocked resources
This is the closest thing to View page as Googlebot today.
Understand About Googlebot User Agent
A Googlebot user agent is the identification string Google’s crawler sends when it visits a webpage.
It tells your server, “This request is coming from Googlebot,” along with information about the device type (like smartphone or desktop). Understanding user agents is important in SEO because websites sometimes serve different content based on who is visiting. If Googlebot is shown different content than users, it can cause indexing issues or even be considered cloaking.
Knowing how Googlebot identifies itself helps ensure your server treats it correctly and that search engines can access your site just like a real visitor would.
So, a user agent is the identifier Googlebot sends when requesting your site.
Example Googlebot smartphone user agent:
Mozilla/5.0 (Linux; Android 10; Pixel 5) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/120.0 Mobile Safari/537.36 (compatible; Googlebot/2.1; +http://www.google.com/bot.html)
Servers use user agents to identify visitors. But some bots fake Googlebot, so Google recommends verifying via IP.
What is Googlebot IP Verification?
While Googlebot identifies itself using a user agent, that alone isn’t always trustworthy because malicious bots can fake it. That’s why Google also uses specific IP address ranges for its crawlers.
IP verification means checking whether a visit claiming to be Googlebot actually comes from Google’s network. This matters for SEO and server management because blocking real Googlebot traffic can prevent your pages from being crawled and indexed, while allowing fake bots can waste server resources.
Verifying Googlebot’s IP ensures your site stays accessible to search engines without opening the door to harmful traffic.
To confirm real Googlebot traffic:
- Take the IP from your server logs
- Run a reverse DNS lookup
- Confirm it ends in googlebot.com or google.com
This prevents fake bots from being mistaken for Google.
Googlebot robots txt
The robots.txt file is the first place Googlebot checks before crawling your website.
It contains rules that tell search engine crawlers which parts of your site they are allowed or not allowed to access.
This makes robots.txt a powerful tool for controlling crawl behavior, especially for large websites with private sections, duplicate content, or low-value pages. However, it’s important to understand that robots.txt only controls crawling, not indexing.
If used incorrectly, it can block important resources like CSS or JavaScript, which may prevent Googlebot from properly rendering and understanding your pages.
So, your robots.txt file controls crawling not indexing directly.
Example:
User-agent: Googlebot
Disallow: /checkout/
Allow: /blog/
Key Points:
- If blocked by robots.txt, Googlebot may not crawl the page
- But the URL can still be indexed if linked elsewhere
- To prevent indexing, use noindex, not robots.txt alone
Googlebot and Noindex
The noindex directive is used to tell Googlebot that a page should not appear in search results, even if it can be crawled.
Unlike robots.txt, which blocks crawling, noindex allows Googlebot to access the page but prevents it from being added to Google’s index. This is useful for thank-you pages, internal search results, or duplicate content that shouldn’t rank.
From an SEO perspective, understanding how noindex works helps you control which pages contribute to your site’s visibility while keeping low-value or private pages out of search.
So, a noindex directive tells Google:
“You can crawl this page, but don’t include it in search results.”
Example:
<meta name=”robots” content=”noindex”>
Important difference:
| Method | Stops Crawling | Stops Indexing |
| robots.txt | ✅ | ❌ |
| noindex | ❌ | ✅ |
How Googlebot Handles JavaScript
Modern websites rely heavily on JavaScript, but this can create SEO problems.
Googlebot:
- Crawls HTML first
- Renders JavaScript later
- May delay rendering if resources are heavy
If key content only appears after JS runs, and rendering fails, Google may miss it.
Best Practice
Use server-side rendering (SSR) or ensure critical content is present in initial HTML.
Googlebot Image & Video Crawling
Google uses special bots:
Googlebot-Image
- Crawls image files
- Uses alt text to understand images
Example:
<img src=”technical-seo-audit.jpg” alt=”Technical SEO audit checklist”>
Googlebot-Video
Understands video content using:
- Structured data
- Video sitemaps
- Metadata
Ensure Googlebot Can Crawl and Render Your Website Pages
Testing Googlebot access means checking whether Google’s crawler can properly reach, crawl, and render your pages.
This involves using tools like Google Search Console’s URL Inspection feature, reviewing robots.txt rules, and sometimes analyzing server logs. The goal is to see your site from Googlebot’s perspective and identify any technical barriers such as blocked resources, crawl errors, or rendering problems.
Regular testing helps ensure that important pages remain fully accessible to search engines, which is essential for maintaining strong search visibility.
Here’s a quick checklist:
✔ Use URL Inspection Tool
✔ Check robots.txt Tester
✔ Review server logs for Googlebot hits
✔ Use site:yourdomain.com searches
✔ Ensure JS/CSS are crawlable
Common Googlebot Issues & Fixes
This section is the backbone of this guide.
Even well-designed websites can face problems that prevent Googlebot from properly crawling or understanding content.
These issues may include blocked JavaScript or CSS files, accidental noindex tags, crawl errors, or pages that rely too heavily on dynamic content. When Googlebot encounters these barriers, it may index incomplete information or skip the page entirely, which can hurt rankings.
Recognizing common Googlebot issues helps you diagnose technical SEO problems early and keep your site fully accessible to search engines.
Let’s break down the common Googlebot issues and how we can fix them:
Issue | Cause | Fix |
Page not indexed | noindex present | Remove tag |
Content missing | JS blocked | Allow scripts |
Broken layout | CSS blocked | Allow styles |
Images not indexed | Missing alt text | Add descriptive alt |
Crawl waste | Infinite filters | Use canonical tags |
FAQ - Googlebot & View Page as Googlebot
Googlebot is Google’s web crawler that discovers and indexes web pages for search results.
It helps you see rendering issues, blocked resources, and indexing problems from Google’s perspective.
No. It only controls crawling. Use noindex to stop indexing.
It’s the identifier string Googlebot sends when requesting a webpage.
Yes, using Search Console’s Live Test and server log analysis.
Google renders JS, but delays or blocked resources can cause indexing issues.
Googlebot uses Google-owned IP ranges that can be verified via reverse DNS.
One crawls images, the other understands video content and metadata.
Final Thoughts
Understanding how Googlebot works is one of the most powerful skills in technical SEO.
When you “view a page as Googlebot,” you stop guessing and start seeing your site the way Google does. That’s how you uncover hidden SEO problems that competitors miss.
If you want better rankings, make sure:
- Googlebot can crawl your pages
- It can render your content
- It’s not blocked by robots.txt or noindex
- Your images, videos, and JS are accessible
Master Googlebot, and you master technical SEO. Tell me where do you stand now?
Ahmad Fraz is a seasoned SEO strategist and digital marketing expert with over 9 years of experience helping brands like Dyson, 3M, Marriott, and CureMD achieve measurable growth. Specializing in technical SEO, content strategy, and data-driven optimization, at Ahmad Fraz SEO, he empowers businesses of all sizes to improve visibility, drive qualified traffic, and achieve long-term digital success. His insights and actionable strategies are backed by years of hands-on experience and proven results.
