You publish a great page. Helpful content, solid design, everything on point… but it never ranks.
Frustrating, right?
Sometimes the problem isn’t your content, it’s your crawl depth. Before Google can rank a page, it first has to find it easily. And if your page is buried too deep inside your website, search engines may not treat it as important.
Let’s break this down in simple terms.
What Is Crawl Depth?
Crawl depth refers to the number of clicks it takes for a search engine bot (like Googlebot) to reach a page starting from your homepage.
Think of your website like a building with basements:
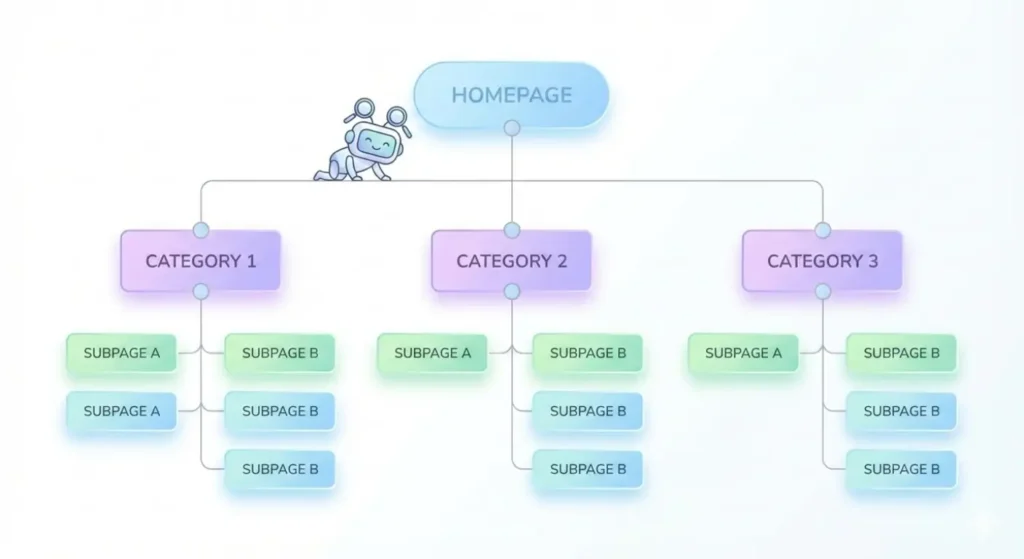
- Homepage = Ground floor (Depth 0)
- Main category page = 1st basement (Depth 1)
- Subcategory page = 2nd basement (Depth 2)
- Individual blog post or product = 3rd basement (Depth 3+)
The more clicks required to reach a page, the deeper its crawl depth.
Crawl Depth vs URL Depth (Important Difference)
People often confuse these two:
Crawl Depth | URL Depth |
Based on internal links | Based on URL folders |
Affects how bots reach pages | Mostly for structure and clarity |
Impacts crawling and indexing | Doesn’t always impact crawling |
A page can have a short URL but still be hard to reach if you don’t link to it properly.
Why Crawl Depth Matters for SEO
Crawl depth SEO is about making sure important pages are easy for search engines to reach. Here’s why that matters:
1- Crawl Budget Efficiency
Google doesn’t crawl every page on your site equally. Pages that are closer to the homepage usually get crawled more often.
2- Faster Indexing
Shallow pages are discovered and indexed quicker than deeply buried ones.
3- Stronger Link Equity Flow
Internal link value weakens as it passes through more layers. Pages closer to the homepage often receive more authority.
Bonus: It’s About Users Too
If it takes Google 5 clicks to reach a page, imagine a real user trying to find it. A flatter structure improves both SEO and user experience.
What Is a “Good” Crawl Depth?
Most guides stay vague here, but let’s make it practical:
Page Type | Ideal Crawl Depth |
Homepage | 0 |
Key category pages | 1 |
Important service/product pages | 1–2 |
Blog posts | 2–3 |
Anything deeper than 4 | Needs review |
If an important page is sitting at depth 5 or 6, it’s probably too buried.
How to Find Crawl Depth in Ahrefs
This is where things get actionable.
If you’re using Ahrefs, you can quickly spot crawl depth issues:
- Run a Site Audit in Ahrefs
- Let Ahrefs crawl your website
- Go to the Internal Pages report
- Add a filter for Crawl depth
- Sort pages by highest depth
Now look for pages that are:
- Important but buried too deep
- Getting little traffic but sit at high depth
If a key page has high crawl depth, it’s a signal you need better internal linking.
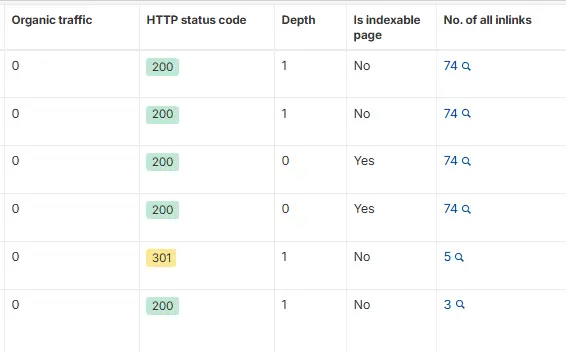
In my case redirection and the pages far from homepage i mean no links from homepage contains crwal depth = 1 otherwise all page including homepage showing crwal depth = 0
Common Crawl Depth Mistakes
Here’s where many sites go wrong:
❌ Orphan Pages
Pages with no internal links pointing to them; Google can barely find them.
❌ Overcomplicated Navigation
Too many subcategories and layers make content harder to reach.
❌ Pagination Traps
Older blog posts get pushed further and further away from the homepage.
❌ Ecommerce Filters
Faceted navigation creates endless deep URLs that waste crawl resources.
How to Fix Crawl Depth (Quick SEO Checklist)
You don’t need to redesign your entire site. Start with these:
✔ Add contextual internal links inside blog content
✔ Link important pages directly from the homepage
✔ Use breadcrumbs for better structure
✔ Flatten overly complex category layers
✔ Create an HTML sitemap
✔ Find and fix orphan pages
✔ Keep important pages within 3 clicks if possible
That “3-click rule” is a solid benchmark for crawl-friendly architecture.
Crawl Depth vs Crawl Budget
These are related but different.
- Crawl depth = how far pages are from the homepage
- Crawl budget = how many pages Google chooses to crawl
Deep pages can waste crawl budgets because Google spends more effort reaching them and may skip some entirely.
The Future of Crawl Depth in SEO
Search engines are getting smarter, but site structure still matters.
With mobile-first indexing and AI-driven crawling, Google prefers sites that are clean, logical, and easy to navigate. A flat, well-linked website sends strong signals about which pages truly matter.
In modern SEO, architecture is strategy.
FAQ - Googlebot & View Page as Googlebot
No. Crawl depth itself isn’t a direct ranking factor, but it strongly influences how easily search engines discover, crawl, and index your pages. Pages that are closer to the homepage usually get crawled more often and have a better chance of performing well.
In most cases, pages deeper than 4 clicks from the homepage are considered too deep. Important pages like services or high-value blog posts should ideally be within 2–3 clicks.
Crawl depth refers to how many clicks it takes to reach a page through internal links, while URL depth refers to the folder structure in the URL. A short URL does not always mean a shallow crawl depth.
You should review crawl depth during regular technical SEO audits, especially after adding new content, redesigning navigation, or expanding categories.
Yes. Adding contextual internal links from high-authority or top-level pages can reduce crawl depth and help search engines reach important pages faster.
Final Takeaway
I tried my best to teach you the most confusing topic of technical SEO. I hope you become able to clear your concepts. Aren’t you?
Moreover, here’s the simple rule:
If a page is important for users, it should be close to your homepage for Google too.
Fixing crawl depth isn’t just a technical tweak; it’s a foundational step toward better rankings, faster indexing, and stronger overall SEO performance.
Ahmad Fraz is a seasoned SEO strategist and digital marketing expert with over 9 years of experience helping brands like Dyson, 3M, Marriott, and CureMD achieve measurable growth. Specializing in technical SEO, content strategy, and data-driven optimization, at Ahmad Fraz SEO, he empowers businesses of all sizes to improve visibility, drive qualified traffic, and achieve long-term digital success. His insights and actionable strategies are backed by years of hands-on experience and proven results.
