Feeling stuck with rankings? This might be why…
Ever had this happen?
- You publish a great piece of content… and it just doesn’t rank
- Some pages get traffic, others feel completely invisible
- Google indexes part of your site but ignores important pages
- A random blog post ranks… but your service page doesn’t
- Your SEO tool says: “Orphan pages detected”
Frustrating, right?
Most people blame:
❌ Content
❌ Backlinks
❌ Competition
But often the real problem is much closer to home…
👉 Your internal linking structure
Think of this guide as a fix for your website’s “road system.” We’re going to help Google move through your site easily and guide users exactly where you want them to go.
Let’s start with the basics.
What Is Internal Linking in SEO?
Internal linking is when one page on your website links to another page on the same website.
Example:
<a href=”https://yoursite.com/technical-seo-checklist”>Technical SEO checklist</a>
That link doesn’t go to another domain, it stays within your site.
That’s an internal link.
Simple concept. Massive SEO impact.
Why Internal Links Matter So Much for SEO
Search engines don’t “see” your site like humans do.
They crawl links to discover and understand your content.
Internal links help Google:
1 – Discover your pages
If nothing links to a page, Google may treat it as unimportant or miss it entirely.
2 – Understand page importance
Pages with more internal links pointing to them are often seen as more important.
3 – Pass authority (link equity)
Strong pages can pass SEO value to other pages through internal links.
4 – Understand topical relationships
If multiple articles link to one guide, Google sees that guide as a core topic page.
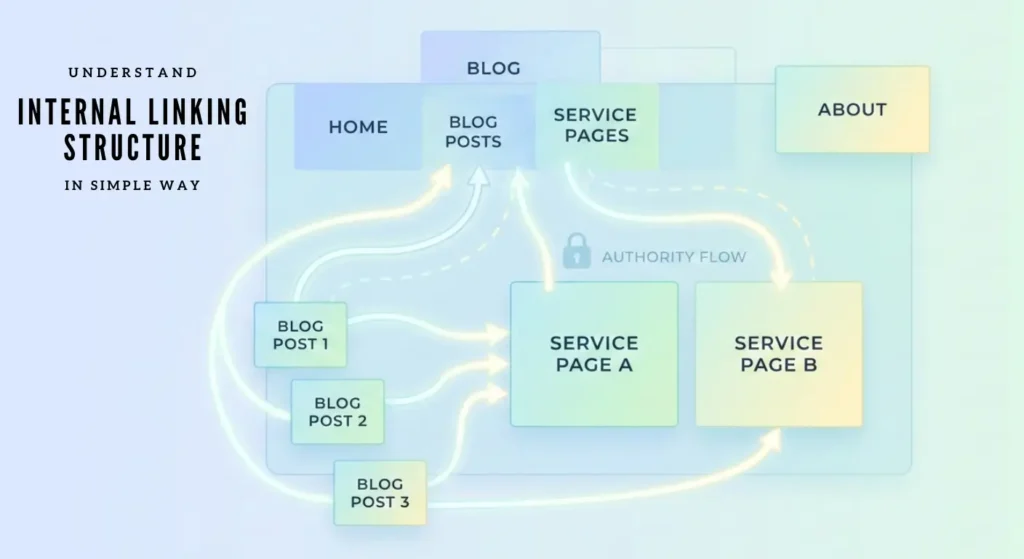
Internal Linking Structure (Made Simple)
Imagine your website like a city:
- Homepage = Downtown
- Category pages = Main roads
- Blog posts = Side streets
- Important guides = Major buildings
Without proper roads (links), nothing connects.
Good internal linking = strong website architecture
What are the Internal Linking Best Practices?
These are the fundamentals that actually move rankings.
Use descriptive anchor text
Bad: Click here
Better: internal linking audit checklist
Search engines use anchor text to understand the destination page.
Link more often to important pages
Your key pages (services, pillar guides, high-value content) should receive more internal links than minor posts.
Fix orphan pages
An orphan page has no internal links pointing to it.
To Google, that page is almost invisible.
Use contextual links
Links placed naturally within content are stronger than sidebar or footer links.
Example:
Before optimizing, review this internal linking audit guide.
Keep crawl depth shallow
Important pages should be reachable within 3 clicks from the homepage.
Homepage → Category → Important Page
Not Homepage → Blog → Archive → Tag → Page 2 → Post
You may love to explore What is Crawl Depth?
How to Do an Internal Linking Audit (Step by Step)
This is where you can outperform most competitors.
Step 1: Run a site audit in Ahrefs or Screaming Frog
Look for:
- Orphan pages
- Pages with very few internal links
Step 2: Find your strongest pages
In Ahrefs, check Best by Links.
These pages have the most authority and should link to important but weaker pages.
Step 3: Review anchor text
Make sure:
- Anchors are descriptive
- You’re not overusing the exact same keyword
Step 4: Combine traffic + link data
Low-traffic + low internal links = opportunity page
Add relevant internal links to boost visibility.
Case Study: Boosting SEO Performance Through Strategic Internal Linking
Website: ahmadfrazseo.com
Focus: Internal linking structure optimization
ahmadfrazseo.com is my personal website, and like many regular clients websites, it was handed over to me by the developer (I hired) with a poor internal linking structure. The difference with an SEO specialist’s approach is that we don’t just focus on creating content, we optimize structure, authority flow, and user experience as well.
In this case study, I’m sharing my personal experience and showing the results achieved through strategic internal linking.
The Challenge
When ahmadfrazseo.com was handed over by the developer, the website looked solid on the surface: well-written content, clear services, and a professional design. But under the hood, the internal linking structure was poor:
- Many blog posts I provide to developer with content) were disconnected from key service pages.
- Some deeper pages had very few links pointing to them.
- Important “money pages” like SEO Services weren’t receiving enough contextual authority.
- Internal links existed, but they were random and non-strategic, lacking hierarchy.
In simple terms: the site had strong buildings (content) but weak roads (internal links) connecting them.
The Goal
The objective was to design an internal linking framework that would:
- Improve crawl efficiency for search engines
- Pass authority from high-value pages to key service pages
- Strengthen topical relevance between blogs and services
- Reduce isolated or orphan pages
Enhance user navigation and engagement
+—————-+
| Homepage |
+—————-+
↓
+————————–+————————–+
↓ ↓ ↓
+————-+ +—————–+ +—————-+
| SEO Portfolio| | SEO Services | | Blog (all posts)|
+————-+ +—————–+ +—————-+
| |
+————————+———————+ |
↓ ↓ ↓ |
+—————-+ +————————+ +———————-+
| Website SEO | | Technical SEO Services | | Internal Linking Blog |
| Audit Service | +————————+ | (example content) |
+—————-+ ↓ +———————-+
|
+—————-+—————-+
↓ ↓
+———————-+ +————————+
| Internal Linking & IA| | Schema Markup Service |
| Audit Service | +————————+
+———————-+
|
↓
+—————————+
| Related Blog/Content Pages|
| (targeted keyword posts) |
+—————————+
The Strategy
A structured internal linking framework was implemented across three layers:
1 – Homepage as the Authority Hub
The homepage became the primary authority source, linking clearly to:
- SEO Services
- SEO Portfolio
- Blog section
This ensured authority flowed naturally from the strongest page to key sections.
2 – Service Pages as Topical Silos
The SEO Services page was treated as a parent hub, linking to:
- Website SEO Audit Service
- Technical SEO Services
- Internal Linking & IA Audit Service
Service pages were also interlinked where relevant, creating a tight service silo that signals topical depth to search engines.
3 – Blog Content Supporting Service Pages
Informational blog posts were leveraged as authority boosters. Each relevant article now links contextually to:
- The most relevant service page
- Related SEO blog posts
- Broader category or pillar content
Example: A blog post about internal linking now supports the Internal Linking & IA Audit Service page via contextual anchor text.
This approach demonstrates to Google that the website does more than talk about SEO, it offers professional services.
Structural Improvements
Before Optimization | After Optimization |
Random internal links | Structured, topic-based linking |
Some orphan or weak pages | All key pages connected within 2–3 clicks |
Blog posts isolated from services | Blogs now support service pages |
Authority concentrated on top pages only | Authority distributed strategically |
Why This Model Works
- Better Crawl Efficiency – Search engines can move logically from general pages to deeper services.
- Stronger Topical Signals – Service pages are reinforced by supporting blog content.
- Authority Flow Control – Internal links now pass value strategically instead of relying solely on backlinks.
- Improved User Journey – Visitors can naturally move from learning (blogs) to action (service pages).
Key Takeaways
Internal linking isn’t just about navigation, it’s SEO architecture.
By restructuring internal links on ahmadfrazseo.com:
- Key pages became easier for search engines to discover
- Service pages gained stronger contextual support
- The site’s overall topical authority became clearer
This case study demonstrates how a smart internal linking strategy can turn existing content into a powerful ranking system without creating new backlinks or rewriting every page.
How to Add Internal Links in HTML?
Basic internal link structure:
<a href=”/internal-linking-guide/”>internal linking guide</a>
Tips:
- Relative URLs are fine
- Avoid using nofollow for internal links
Opening internal links in a new tab usually isn’t necessary
Common Internal Linking Mistakes
Adding too many links
- Stuffing links into every sentence looks spammy and reduces value.
Repeating the same anchor text
- Over-optimization can send unnatural signals.
Only linking to the homepage
- Authority should flow to deeper pages too.
Broken internal links
- Bad for UX and wastes crawl budget.
What are the Best Tools for Internal Linking in SEO?
Tool | What It Helps With |
Ahrefs | Internal link reports, orphan detection |
Screaming Frog | Crawl depth & structure analysis |
Google Search Console | Top internally linked pages |
Link Whisper (WordPress) | Internal link suggestions |
Advanced Internal Linking Strategies
Want to go beyond basics?
Topic Clusters
- Create one pillar page and multiple supporting articles that all link together. This builds topical authority.
Authority Flow Strategy
- Link from pages with strong backlinks to your money or conversion pages.
Update old content
- When you publish a new post, go back and add links from older relevant articles. This gives new pages a fast visibility boost.
Internal Linking Is SEO Control
You can’t fully control backlinks.
You do control internal links.
They influence:
- How Google crawls your site
- Which pages seem most important
- How authority flows
- How users navigate
When internal linking is done right, rankings often improve quietly — even without new backlinks.
For many growing websites, building an effective internal structure takes time, planning, and ongoing analysis. That’s why many businesses choose professional internal linking services to audit their site architecture, fix orphan pages, and strategically distribute authority to the pages that matter most. When done correctly, this isn’t just about adding links — it’s about building a structure that helps both users and search engines move through your site effortlessly.
FAQ - Internal Linking in SEO
Internal linking is the process of linking one page of your website to another page on the same domain. These links help search engines discover content, understand site structure, and pass authority between pages.
Internal links help search engines crawl your website more efficiently, distribute link equity, and understand which pages are most important. They also improve user navigation and increase time on site.
There is no exact number, but links should be added naturally where relevant. The goal is to help users and search engines, not to stuff links excessively.
Orphan pages are pages that have no internal links pointing to them. These pages are hard for search engines to discover and usually struggle to rank.
Descriptive and contextually relevant anchor text works best. Instead of using “click here,” use keywords that describe the linked page.
Yes. Internal links pass link equity (ranking power) from stronger pages to weaker ones, helping improve overall site performance.
Generally, internal links should open in the same tab to maintain a smooth user experience and clear navigation flow.
You can use tools like Ahrefs, Screaming Frog, or Google Search Console to find orphan pages, broken links, and pages with too few internal links.
Final Thought
Internal linking might not be flashy…
But it’s one of the most powerful SEO levers you fully control.
Fix your internal structure, and you make your site easier for both users and search engines to understand — and that’s exactly what Google rewards.
Ahmad Fraz is a seasoned SEO strategist and digital marketing expert with over 9 years of experience helping brands like Dyson, 3M, Marriott, and CureMD achieve measurable growth. Specializing in technical SEO, content strategy, and data-driven optimization, at Ahmad Fraz SEO, he empowers businesses of all sizes to improve visibility, drive qualified traffic, and achieve long-term digital success. His insights and actionable strategies are backed by years of hands-on experience and proven results.
